When it comes to Forex trading, price is not only moved by charts and technical setups.
Behind the candles, there are powerful forces — the fundamentals.
Michael Huddleston (ICT) often emphasizes that while charts show you entries and exits, it’s the macro fundamentals that create the environment for price to move in the first place.
Let’s break down four important factors in Forex fundamental analysis, focusing on economic reports and GDP, and see how they influence the market.
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
GDP measures the total value of goods and services produced in a country. In simple terms, it shows how strong or weak an economy is.
- A growing GDP signals economic strength, which usually makes the country’s currency more attractive.
- A shrinking GDP shows weakness, often leading to a weaker currency.
Example: If US GDP numbers come out stronger than expected, traders might buy USD against weaker currencies like the Euro or Yen.
On the other hand, if GDP is lower than forecast, the USD may drop.
ICT traders see GDP as a broad driver of bias. For example, if the US shows strong growth while the Eurozone struggles, ICT would lean towards long USD/short EUR setups when technical models confirm.
2. Employment Data (Non-Farm Payrolls – NFP)
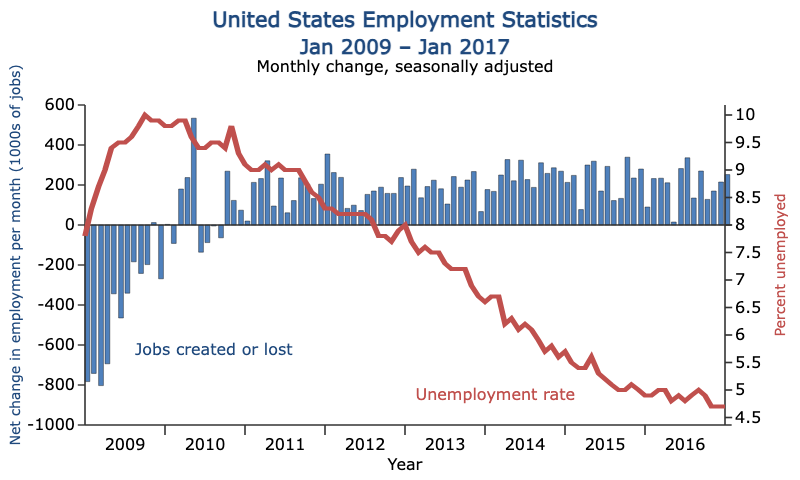
One of the most watched reports in Forex is the US Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP), which comes out on the first Friday of every month.
It measures job creation in the US, excluding farm work.
- High job growth = stronger economy, likely stronger USD.
- Low job growth = weaker economy, likely weaker USD.
Example: Suppose NFP shows 300,000 new jobs created when the forecast was only 200,000.
This surprise could cause USD to rally sharply against other currencies.
ICT traders don’t just chase the spike.
Instead, they watch how liquidity pools are engineered around these reports — for example, stop runs before the release and then the “real” move after the data.
3. Inflation Reports (CPI – Consumer Price Index)
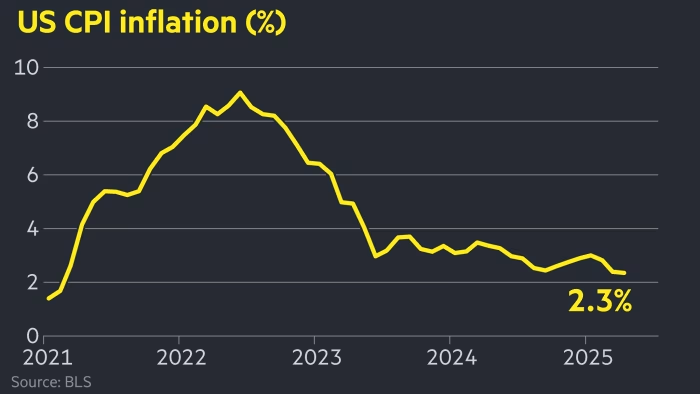
Inflation measures how much prices are rising in an economy.
Central banks like the Federal Reserve (Fed) or the European Central Bank (ECB) use inflation data to decide interest rates.
- High inflation often forces central banks to raise rates, which supports the currency.
- Low inflation or deflation may lead to lower interest rates, weakening the currency.
Example: If US inflation (CPI) comes out at 5% while the forecast was 4%, traders may expect the Fed to raise rates.
This anticipation can push USD higher.
ICT emphasizes that these reports create narratives.
Smart money often uses CPI releases to engineer liquidity — creating false moves first before driving price in the intended direction.
4. Central Bank Interest Rate Decisions
Ultimately, GDP, employment, and inflation reports feed into one main driver: central bank policy.
Interest rates directly impact currency value.
- Higher rates attract foreign capital, strengthening the currency.
- Lower rates push money out of the economy, weakening the currency.
Example: If the European Central Bank unexpectedly raises rates, EUR/USD might shoot up.
Conversely, if the Fed cuts rates, USD could fall across the board.
ICT traders understand that central banks don’t move randomly.
They look at fundamentals (GDP, jobs, inflation) to justify rate decisions.
But on the chart, ICT shows us how these big events are used to run stops and fill orders.
5. How ICT Uses These Factors
ICT’s perspective is not just about reading the news. Instead, it’s about:
- Knowing which reports are most important.
- Understanding the narrative behind them.
- Watching how liquidity pools are formed around these events.
- Using technical setups (like Fair Value Gaps, Order Blocks, Liquidity Runs) to execute trades after fundamentals provide direction.
6. Conclusion
Forex is driven by more than just technical analysis. Fundamentals like GDP, jobs data, inflation, and interest rates set the stage for price movements.
ICT traders use these reports to understand bias, while still relying on technical precision for entries and exits.
The key takeaway is this: fundamentals tell you why the market is moving, while ICT’s technical framework shows you how to trade it.

Leave a Reply