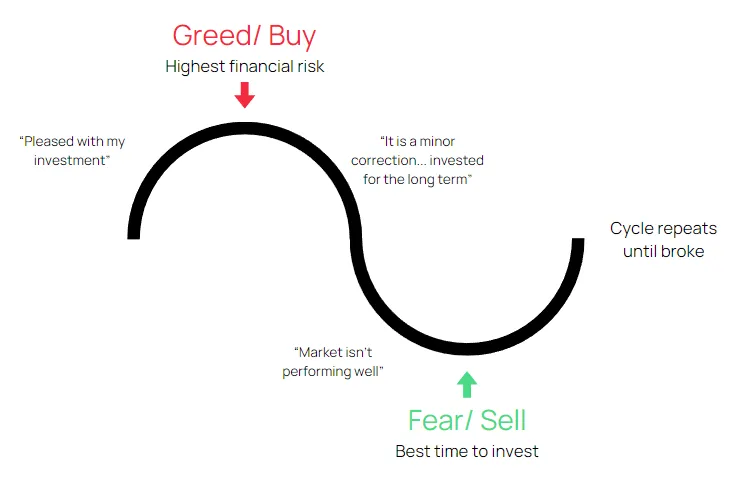
Fear and greed are two of the most common emotional pitfalls for retail traders.
They often lead to impulsive decisions, overtrading, or hesitating at critical moments.
The Inner Circle Trader (ICT) methodology provides a structured approach that can help traders mitigate emotional interference by focusing on institutional trading concepts and disciplined strategies.
1. How Fear and Greed Affect Retail Traders in ICT

- Fear:
- Traders exit winning trades too early, fearing a reversal.
- They hesitate to enter valid setups, missing opportunities.
- Fear of loss causes over-reliance on indicators and untested strategies.
- Greed:
- Traders hold losing trades too long, hoping for a reversal.
- Overleveraging or overtrading to maximize gains leads to account blowouts.
- Jumping into trades impulsively without proper analysis.
2. ICT Methods to Counter Fear and Greed
1. Rely on Market Structure and Price Action
- ICT emphasizes analyzing market structure, focusing on higher highs, higher lows, and break of structure (BOS) to identify trends.
- Example: If GBP/USD breaks a previous resistance level and forms a higher high, ICT methods suggest waiting for a retracement to enter, reducing fear of missing out (FOMO).
2. Use Order Blocks for Precision
- Order blocks are institutional zones of interest where large orders are placed.
- By focusing on these zones, traders avoid impulsive entries and gain confidence in their setups.
- Example: Instead of chasing a breakout, wait for price to return to a bullish order block before entering a long trade.
3. Set Predefined Rules with ICT Concepts
- ICT encourages predefined rules, such as:
- Only trade during ICT kill zones (e.g., London Open or New York Open).
- Use optimal trade entries (OTE) for high-probability setups.
- Example: During the New York Open, if EUR/USD aligns with a fair value gap (FVG) and optimal trade entry, execute the trade without hesitation.
4. Stop Loss and Risk Management

- ICT strategies enforce strict stop-loss placement based on liquidity levels or recent swing highs/lows.
- Example: For a short trade, place your stop loss above a liquidity sweep to avoid emotional exits during minor pullbacks.
5. Target Institutional Levels
- ICT teaches traders to set targets based on institutional price levels or liquidity pools instead of arbitrary points.
- Example: If a sell-side liquidity pool is visible, set your take-profit level just above it, reducing the temptation to hold for more.
3. Practical Examples of Avoiding Emotions with ICT

Scenario 1: Fear of Entering a Trade
- A trader sees EUR/USD in an uptrend but hesitates to enter after a retracement. Using ICT, they identify a bullish order block at 1.1000 and place a limit order.
- The structured plan eliminates hesitation caused by fear.
Scenario 2: Greedy Overtrading
A trader profits from a sell-off in GBP/USD and feels tempted to re-enter after the move ends.
ICT methodology encourages waiting for price to return to a fair value gap or liquidity sweep before considering another trade, avoiding impulsive entries.
4. Tips to Cultivate Discipline with ICT

- Focus on One or Two ICT Strategies:
- Master concepts like order blocks or liquidity pools before adding more strategies to your arsenal.
- Maintain a Trading Journal:
- Log trades, including emotions experienced during trades, to identify patterns of fear or greed.
- Avoid Overtrading:
- Stick to pre-planned trades based on ICT kill zones and setups.
- Practice on a Demo Account:
- Backtest ICT strategies to build confidence and reduce emotional stress in live trading.
5. Final Thought
By following ICT’s systematic and rule-based approach, traders can significantly reduce emotional decision-making.
Fear and greed become secondary to executing well-defined, high-probability setups rooted in institutional trading concepts.
This methodical approach provides clarity, confidence, and consistency, ensuring long-term success in trading.

Leave a Reply